Movement observed, ‘captured’ and distorted
An animator must imagine every aspect of the image and its motion. This reliance on imagination frees the animated form from the necessity of real life observations as in the early experiments with visual music. The history of commercial animation started with the studios set-up by the Disney brothers, Warner brothers and Max Fleischer in the early 1900s, Max Fleischer studios (creators of Betty Boop) were keen to explore the plasticity of drawn line and more experimental forms and Oskar Fischinger worked on Disney’s most experimental and inventive film, Fantasia.
However commercial animation has predominantly been built on a highly representational approach. The decomposition and re-composition of real movements recorded by the camera became an integral part of Disney’s animation-making process, along with other studios at the time. Animators in Walt Disney studios would shoot live action films, make what they call ‘photostats’ (which were separate reprints of blown-up frames in the form of a flipbook) and study the movements frame-by-frame. Animators attended life-drawing classes, and used Edweard Muybridge’s sequential photographs of movement to study motions of animals (Muybridge was an English photographer important for his pioneering work in photographic studies of motion, and early work in motion-picture projection).
However these techniques generally produce lifeless results that do not communicate clearly to the viewer. (see discussion of rotoscoping in Project 3.4) The questions of what to leave out and what short-cuts to take are the key creative decisions in making animation readable and also have emotional story-telling impact. Drawing classes at Disney and other studios therefore started to focus on more expressive principles of animation involving distortion, simplification and amplification of observed movement.
TASK:
Make at least three loops to explore the principles of ‘squash and stretch’ and ‘anticipation and overshoot’. Work fast, loose and expressively in any medium. Push your approach by overly distorting or exaggerating these movements, as well as refining them to their essential qualities.
Upload your GIFs to your learning log along with any research.
These principles focus particularly on:
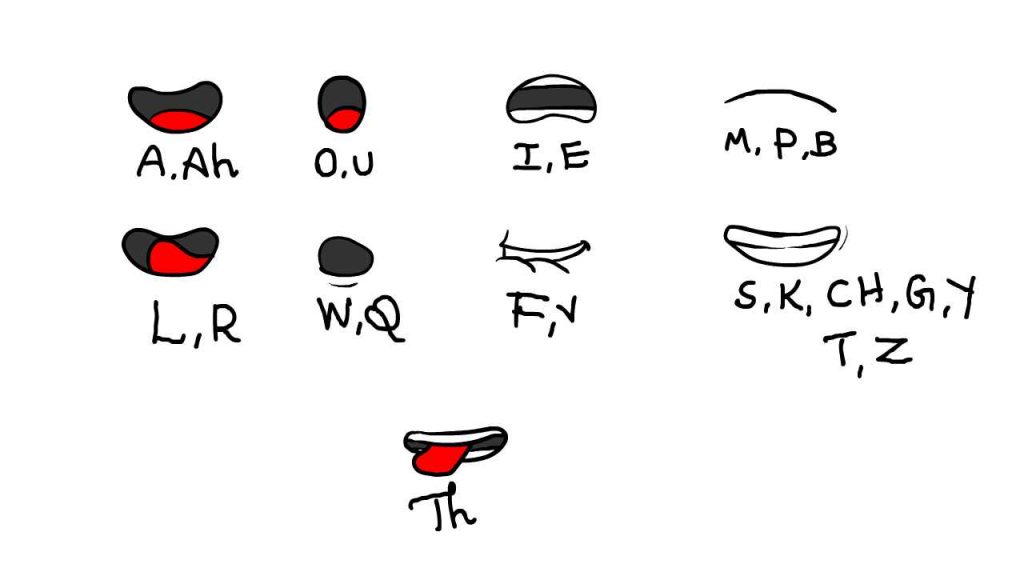
Instability of line: As a general rule, to add life to a drawing, the identity of line should be unstable. The unstable line implies movement, breath, what we know to be life-like as in the discussion of ‘Boil’ in Project E1.2 and Research 1.1.
Exaggeration: The most common form of this exaggeration is known as ‘squash and stretch’ where a shape is distorted to indicate the impact of gravity and energy, and also to reflect the effects of motion blur in our perception of movement. Including a frame or two of anticipated movement where the first frame of the movement moves in the opposite direction of the
movement to give an illusion that the movement is ‘self-motivated’. This also allows the viewer’s eye to momentarily register that a movement is about to take place so that it can be the point of focus and viewed without being missed. This is then enhanced further by frames of ‘overshoot’ and ‘follow-through‘ representing movement of items like clothing, tails, hair etc and attention to secondary movement.
See detailed discussion of Disney animation principles on VisCom4Dev blog.
Swarm Fireflies
My first exercise was done in Adobe Animate in response to activities suggested on my on-line Animation Academy practical animation course with Howard Wimshurst. This involved experiments in timing and positioning of dots in relation to each other to create a ‘swarm’. Then experimenting with shape and lengthening the lines to create an illusion of rapid movement without strobing.
This was very interesting in demonstrating that animation is not about producing a series of sequential still frames, but creating images that show movement in themselves. Many of which may well not make sense when viewed individually outside the running sequence.
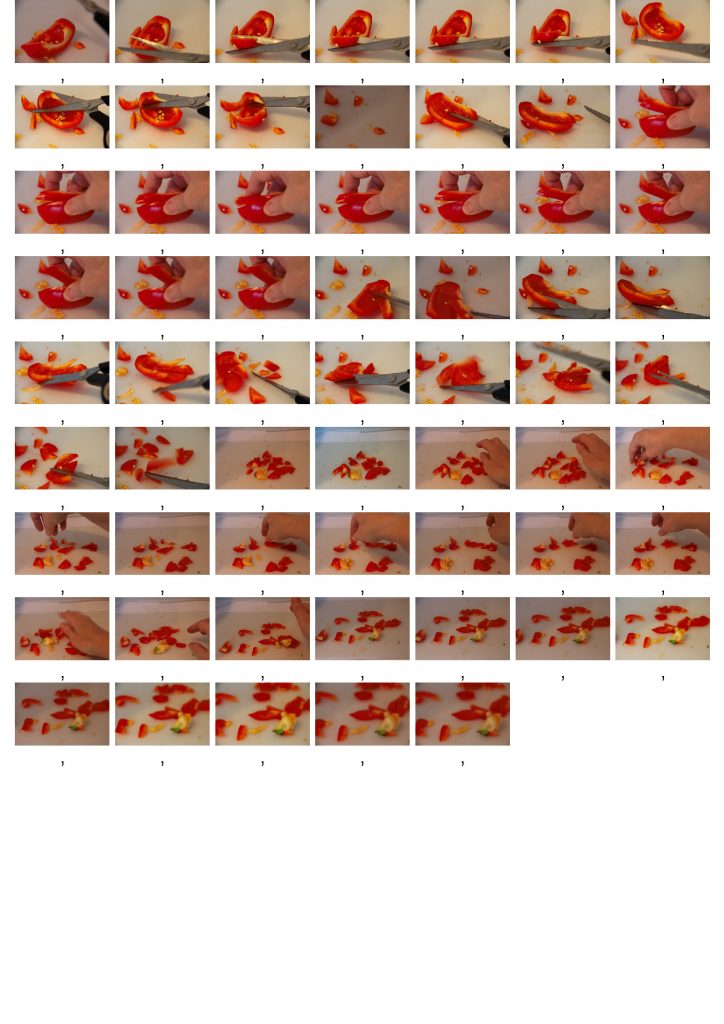
Stop Motion Squash and Stretch
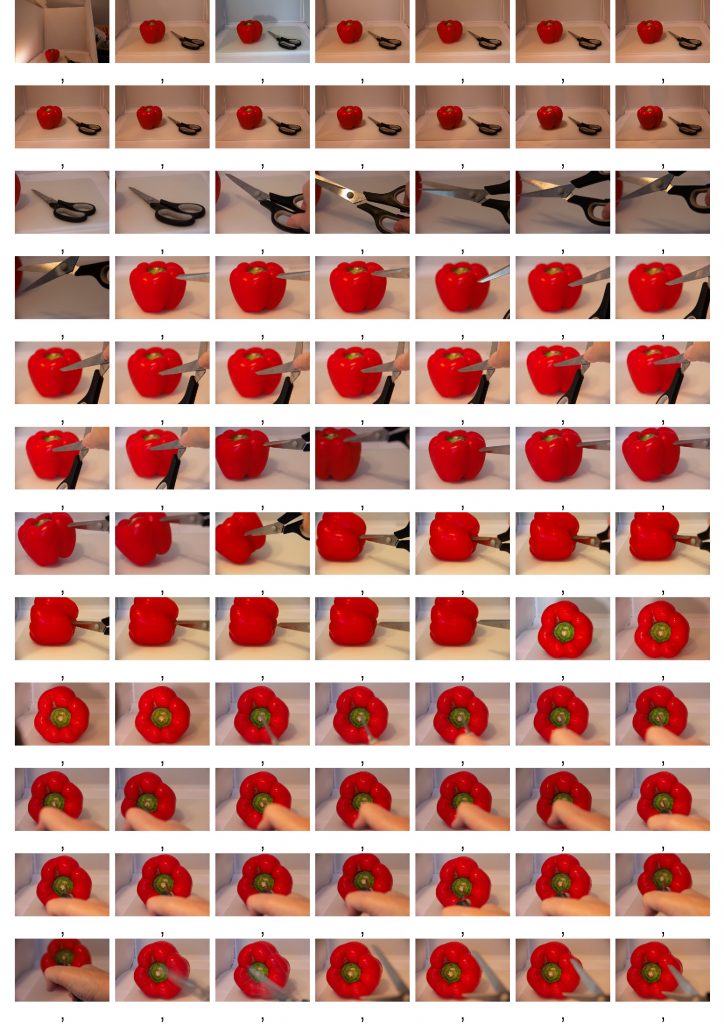
Animation principles in Frame by Frame animation are explored in detail in my OCA Visual Communications degree courses. So for the other two animations I decided to see how things might work using Stop Motion, building on my materials explorations different materials in E2.1 Material Performance and with peppers and cabbage in Part 1 and and E2.4 Lip Sync.
These experiments were quite interesting, and could be effective with a comic or allegorical narrative and a more interesting background. But I need a lot more practice to get smoother movement and then edit with time remapping in After Effects or Premiere. I could also experiment more with lighting – physical and/or digital – as in Death of a Cabbage.